Payment gateways are critical in the quickly changing environment of online purchases, providing safe and frictionless financial transactions. A payment gateway is simply a technology-driven solution that functions as a go-between for an online merchant and the financial institutions that process transactions. Its major duty is to securely approve and validate the transfer of money from the customer’s bank to the merchant.
What is a Payment Gateway?
A payment gateway is a technical infrastructure that allows for secure exchange of financial information between a website or mobile application and a payment processor. It functions as a bridge, allowing online companies to collect payments from clients over the internet. A payment gateway’s principal role is to securely approve and execute transactions while maintaining the security and integrity of sensitive financial data.
How Payment Gateways Work?
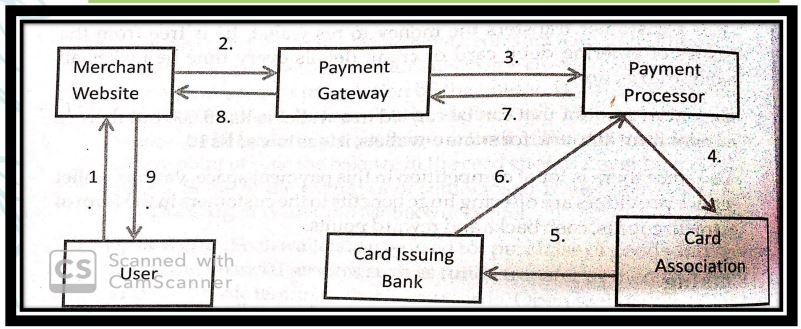
Initiation of Transaction:
The transaction process starts when a client makes a purchase via an online platform. After choosing items or services, the consumer travels to the checkout page, where payment information is input. This information normally contains credit card information, but it may also include alternative payment methods.
Secure Data Transmission:
When a consumer provides their payment information, the payment gateway is activated. It encrypts sensitive data using protocols like Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS). This encryption guarantees that the customer’s data is safeguarded while it travels from the browser to the merchant server.
Merchant’s Server and Payment Gateway Interaction:
The payment information is encrypted and sent from the customer’s smartphone to the merchant’s server. The payment gateway connects to the merchant’s server, decrypts the data, and prepares it for onward transmission to the payment processor.
Payment Processor Authorization:
The payment processor, which is often connected with the financial institution, gets the encrypted transaction information from the payment gateway. It then begins the authorization procedure by ensuring that the payment information given is correct. This includes reviewing the customer’s account balance, ensuring that the credit card has not been reported for fraud, and confirming that there are no other difficulties that might impede the transaction.
Transaction Authorization Response:
The payment processor returns an authorization response to the payment gateway. If the transaction is accepted, the payment gateway notifies the merchant’s server, enabling the purchase to be completed. In the event of a decline, the consumer is typically contacted, and the transaction is not completed.
Real-time Transactions:
In real-time transactions, the whole process—from consumer initiation to authorization—takes just seconds. This is characteristic of most online retail transactions, ensuring that the client has a smooth and quick experience.
Delayed Transactions:
Some transactions, particularly in the travel and event booking industry, may experience delays. In these circumstances, the payment gateway collects the customer’s payment information during the first booking. However, the actual settlement and transfer of monies may take place at a later point, such as when the service is provided or the event occurs.
Understanding the step-by-step breakdown of the transaction process, the critical authorization and verification stages, and payment gateways’ flexibility in handling both real-time and delayed transactions provides insight into how these systems work in the digital payment landscape.
Also read: Top 10 Basic Principles of Personal Finance
Why You Should Use a Payment Gateway?
Businesses and customers may both profit greatly from using payment gateways in the digital payment ecosystem. Here are some strong arguments for adopting and using payment gateways.
1. Enhanced Security Measures:
Payment gateways use sophisticated security protocols like Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption to protect sensitive financial data. This assures that consumer data, including credit card information, is kept secret and secure throughout online purchases. Businesses that use a payment gateway may develop confidence with their consumers while reducing the risk of data breaches and fraudulent activity.
2. Reduced Fraud Risk:
Payment gateways help to avoid fraud by monitoring transactions in real time and using advanced fraud detection systems. Suspicious transactions and abnormalities are quickly discovered, allowing for swift action. This proactive strategy dramatically minimizes the danger of fraudulent activity, giving companies and consumers a safe online environment.
3. Convenience and Efficiency:
Payment gateways provide organizations with a simplified and effective approach to execute transactions. Payment gateways are often seamlessly integrated with e-commerce platforms and websites, resulting in a simple checkout process. This efficiency translates into higher client satisfaction, which may boost conversion rates for online enterprises.
4. Global Reach and Acceptance:
Payment gateways allow companies to accept payments from clients all around the globe, therefore increasing their market reach. Businesses may respond to different client preferences by accepting a variety of payment methods, such as credit cards, debit cards, and other payment choices. This adaptability is particularly important in the increasingly globalised world of e-commerce.
5. Transaction Tracking and Reporting:
Payment gateways provide organizations useful capabilities for monitoring and reporting transactions. This provides real-time information on successful payments, pending transactions, and comprehensive financial reports. Such insights enable firms to track their financial health, reconcile transactions, and make educated choices to improve operations.
6. Enhanced Customer Experience:
For clients, the simplicity of utilizing payment gateways improves their whole online buying experience. The capacity to conduct secure and timely transactions promotes confidence and loyalty. Furthermore, accepting a variety of payment options accommodates a wide range of client preferences, making the purchase process more inclusive and flexible.
7. Streamlined Refund Process:
Payment gateways often give features to help firms handle refunds more smoothly. In the case of a return or cancellation, companies may swiftly execute refunds using the same payment method, offering a simple and transparent settlement for consumers.
In conclusion, payment gateways benefit both companies and consumers. Payment gateways play an important role in the efficiency, security, and general success of online transactions in the digital age, from enhanced security measures to worldwide reach and the ease of accepting many payment methods.
Also read: The ABCs of Personal Finance: Top 10 Essential keys for financial success
Is It Possible to Have Multiple Payment Gateways?
Yes, it is feasible and, in some situations, advantageous to include numerous payment gateways into an e-commerce platform or online company. This strategy, known as employing several payment channels, has various benefits:
1. Redundancy and Reliability:
Integrating several payment gateways gives redundancy. If one payment gateway has technical difficulties or outages, the system may easily transition to an other gateway, guaranteeing that transactions can be completed. This redundancy increases the overall dependability of the payment processing system.
2. Global Reach and Currency Support:
Different payment gateways may specialize in servicing certain areas or currencies. Businesses that integrate different gateways may serve to a global consumer base while also offering localized payment choices. This is especially beneficial for international e-commerce, since it allows firms to cater to the unique tastes and payment methods of clients from different locations.
3. Diversifying Payment Options:
Customers’ payment habits differ. Some people choose to pay using credit cards, while others prefer digital wallets, bank transfers, or other alternative payment methods. Integrating various payment gateways allows companies to provide a wide range of payment options, increasing customer satisfaction and perhaps extending their client base.
4. Optimizing Transaction Costs:
Payment gateways may have different charge structures and transaction costs. By integrating numerous gateways, organizations may strategically route transactions via the gateway with the best terms for a certain transaction type or region. This optimization might result in cost savings for the firm.
5. Adaptability to Market Changes:
New payment methods and technology emerge on a regular basis, making the payment environment dynamic. Integrating numerous payment channels enables firms to respond rapidly to market developments by offering the most recent and popular payment choices. This flexibility helps that firms stay competitive and relevant to changing client demands.
6. Mitigating Risk and Compliance:
Some businesses or areas may have unique regulatory requirements or a greater risk of fraud. Integrating various payment gateways allows organizations to adopt extra security and compliance features, lowering the risk associated with online transactions.
While integrating several payment gateways provides many advantages, companies must carefully consider their particular objectives, target audience, and the expenses associated with each gateway. The implementation should be smooth for users, offering a good and consistent experience regardless of payment method. Businesses should also consider technological compatibility, customer support, and scalability when selecting payment gateways to guarantee a strong and adaptable payment processing infrastructure.
Also read: Maximize, Minimize, Optimize: The ABCs of Credit Cards Strategy
Can You Trust Payment Gateways with Your Financial Data?
Concerns regarding financial data security are understandable, particularly when doing transactions online. However, reputable payment gateways use strong security procedures to protect sensitive data. Here’s a summary of frequent issues, industry-standard security standards, and how to recognize a safe payment gateway:
Common Concerns
- Data Breaches: There is a fear that payment gateways might be susceptible to data breaches, exposing customer information.
- Fraud and Unauthorized Access: Concerns about unauthorized access leading to fraudulent activities and transactions.
- Data Storage Practices: Worries about how payment gateways store and handle sensitive financial data.
Industry-Standard Security Protocols
- Encryption: Reputable payment gateways utilize encryption technologies such as Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) to protect data transfer between the client, merchant, and financial institution.
- Tokenization: Many payment gateways use tokenization, which replaces sensitive information with unique tokens. Even if intercepted, these tokens are useless to prospective attackers.
- PCI DSS Compliance: Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance is a set of security rules intended to guarantee that all businesses that accept, handle, store, or transmit credit card information operate in a secure environment.
How to Identify a Secure Payment Gateway
- PCI DSS Certification: Make that the payment gateway is PCI DSS compliant. This accreditation confirms that the gateway meets industry requirements for securely processing credit card information.
- Encryption Practices: Look for information on the encryption mechanisms employed by the payment gateway. Look for SSL or TLS encryption to ensure that your data is sent securely.
- Tokenization Implementation: When a payment gateway uses tokenization, it provides an additional layer of protection. Determine if this functionality is part of the gateway’s security measures.
- Reputation and Reviews: Research the payment gateway’s reputation. Look for feedback and testimonials from other companies that have utilized the service. A well-known and reputable gateway is more likely to emphasize security.
User Education and Best Practices
- Secure Passwords: As a user, ensure you use strong, unique passwords for your accounts on the payment gateway.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Whenever possible, enable two-factor authentication for an additional layer of security.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep a close eye on your financial statements and transactions. Report any suspicious activities promptly.
Finally, although worries about the security of financial data are genuine, utilizing reputable and accredited payment gateways considerably reduces the risks. Understanding existing security mechanisms, verifying compliance with industry standards, and implementing best practices all contribute to a safe online payment environment for both companies and consumers. Always emphasize security when choosing a payment gateway, and be aware about the safeguards in place to secure your financial information.
Methods to Integrate Payment Gateways
Hosted Payment Pages
- Overview: In this method, customers are redirected to a secure page hosted by the payment gateway to complete the transaction.
- Pros: Simplifies the integration process, as the payment gateway handles the entire payment flow. Reduces security concerns for the merchant.
- Cons: Limited customization of the payment page, potentially leading to a less seamless user experience.
API Integration
- Overview: Application Programming Interface (API) integration allows businesses to integrate the payment gateway directly into their website or application, offering a more seamless user experience.
- Pros: Greater customization, control over the payment process, and the ability to create a consistent brand experience.
- Cons: Requires more development effort, and security responsibilities are shared between the merchant and the payment gateway.
JavaScript Integration
- Overview: Similar to API integration, but JavaScript is used to embed the payment form directly into the website.
- Pros: Combines the customization benefits of API integration with a simplified development process.
- Cons: Requires careful handling of sensitive data and security measures to prevent potential vulnerabilities.
Mobile SDKs
- Overview: Software Development Kits (SDKs) are provided by payment gateways to facilitate integration into mobile applications.
- Pros: Tailored solutions for mobile platforms, enhancing the user experience on smartphones and tablets.
- Cons: May require additional development effort for compatibility with various mobile operating systems.
Choosing the Right Integration Method
- Consider Business Size and Complexity: Smaller businesses may find hosted payment pages more convenient, while larger enterprises with specific requirements may opt for API integration.
- Development Resources: Assess the availability of development resources and technical expertise. Businesses with skilled developers may prefer API or JavaScript integration for more control.
- Security Concerns: Evaluate the sensitivity of the transactions and the level of security required. Hosted solutions may be more suitable for those prioritizing simplicity and security.
Ways Payment Gateways Impact User Experience
1. Speed and Reliability:
- The speed of transaction processing has a substantial impact on user experience. Payment gateways with fast processing speeds contribute to a smooth checkout experience, which reduces the probability of consumers leaving their carts.
- Reliability is key. Users want transactions to be executed without mistakes or delays, which builds confidence in the payment system and the broader company.
2. Choice of Payment Methods:
- Payment gateways improve user experience by providing several payment options. Catering to varied tastes increases user happiness and assures a larger consumer base.
3. User-Friendly Interfaces:
- A well-designed payment gateway interface improves user experience. Clear directions, simple navigation, and visually attractive features all help to make the payment process more user pleasant.
4. Responsive Design:
- Responsive design guarantees payment channels work flawlessly across all devices and screen sizes. This versatility is critical for customers who access the platform via smartphones, tablets, or desktop PCs.
5. Security Measures:
- Users value security for their financial information. Payment gateways that adopt strong security features, such as encryption and fraud detection, help consumers trust and believe in their transactions.
6. Transparent Communication:
- Ensure clear information regarding payment details, such as costs, return policies, and authentication methods. Transparent communication leads to better user comprehension and happiness.
Finally, the choice of payment gateway and integration mechanism has a direct influence on the user experience. A well-thought-out strategy, focused on speed, dependability, user-friendly interfaces, responsive design, and open communication, ensures that the payment process meets user expectations and adds positively to the whole online experience.
Top Payment Gateways in 2024
1. Stripe
- Description: Stripe is known for its developer-friendly approach, and it provides a comprehensive payment gateway solution with a strong set of APIs. It accepts a variety of payment options, including credit cards and digital wallets.
- Unique Features: Seamless integration, customizable checkout experiences, and extensive support for international transactions.
- Considerations: Ideal for businesses seeking flexibility and customization in payment processing.
2. PayPal
- Description: A widely recognized and trusted payment gateway, PayPal caters to both businesses and consumers. It supports online payments, invoicing, and peer-to-peer transactions.
- Unique Features: Buyer and seller protection, one-touch payments, and a user-friendly interface.
- Considerations: Suitable for businesses of all sizes, particularly those with an international customer base.
3. Square
- Description: Square is known for its simplicity and user-friendly design. It offers a range of solutions, from point-of-sale systems to online payment processing.
- Unique Features: Square Reader for in-person transactions, comprehensive reporting tools, and straightforward pricing.
- Considerations: Suited for small to medium-sized businesses with both online and offline sales.
4. Authorize.Net
- Description: A long-standing player in the payment gateway space, Authorize.Net provides a secure platform for online and mobile payments.
- Unique Features: Advanced fraud detection, subscription billing support, and a virtual point of sale (VPOS) system.
- Considerations: Ideal for businesses requiring robust security features and subscription-based billing.
5. Adyen
- Description: Adyen is a global payment company offering an end-to-end infrastructure for seamless payment processing.
- Unique Features: Single platform for online, in-app, and in-store payments, support for numerous payment methods, and dynamic currency conversion.
- Considerations: Suitable for large enterprises with a global presence and complex payment needs.
Required Materials for Payment Gateway Integration
1. Business Information:
- Legal business name, address, and contact details.
- Tax identification number or employer identification number.
2. Bank Account Information:
- Bank account details for fund transfers.
3. Website and Product Information:
- URL and a brief description of the business website.
- Details about products or services offered.
4. SSL Certificate:
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificate for encrypting data during transactions.
5. API Keys and Credentials:
- Unique API keys and credentials provided by the payment gateway for integration.
Compliance Requirements and Legal Considerations
1. PCI DSS Compliance:
- Ensure compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) to protect cardholder data.
2. Terms of Service and Privacy Policy:
- Clearly define terms of service and privacy policies related to the collection and use of customer data.
3. Chargeback Policies:
- Establish transparent chargeback policies and procedures to handle disputes.
4. Regional Compliance:
- Adhere to regional and international regulations, considering data protection laws and currency regulations.
5. Contractual Agreements:
- Review and sign contractual agreements with the chosen payment gateway, understanding terms and fees.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Payment Gateways
1. Optimizing Payment Gateway Content:
- Use NLP to enhance the clarity of payment instructions and notifications.
- Implement sentiment analysis to gauge user satisfaction and address concerns proactively.
2. Enhancing User Experience through Language Processing:
- Implement chatbots with natural language understanding to provide real-time assistance.
- Use language processing to personalize communication, creating a more user-centric experience.
3. Fraud Detection:
- Leverage NLP for analyzing patterns in communication to identify potential fraud or phishing attempts.
4. Customer Feedback Analysis:
- Use NLP tools to analyze customer feedback and reviews for continuous improvement in payment gateway services.
Incorporating NLP into payment gateways not only optimizes content and communication but also contributes to a more intuitive and user-friendly experience, enhancing customer satisfaction and trust in the payment process.
FAQs:
Look for visual cues like the padlock icon in the address bar and ensure the URL starts with "https." Additionally, opt for reputable payment gateways with a track record of adhering to industry-standard security protocols. Absolutely! Integrating multiple payment gateways offers flexibility and caters to a diverse customer base. Just ensure seamless integration and consider the preferences of your target audience. Essential documents include business licenses, bank statements, and tax identification numbers. However, specific requirements may vary, so it's advisable to check the documentation checklist of your chosen payment gateway.How do I know if a payment gateway is secure?
Can I use multiple payment gateways for my online store?
What documents do I need for payment gateway integration?
Also read: How to Save Money: Top 25 the best tips for Building Your Savings




